Misuratore di energia auto-configurato (*si applicano termini di supporto speciali)
Quando il tuo misuratore di energia ha indirizzi modbus configurabili (o quando il tuo misuratore di energia non è nell'elenco dei dispositivi supportati), forniamo una funzionalità per configurare un misuratore di energia da solo. È un processo che ti consente di impostare il misuratore di energia come schiavo modbus, permettendogli di comunicare con il SmartgridOne Controller.
*Si prega di notare che questa funzionalità è fornita "così com'è" e deve essere utilizzata a tuo rischio. Se riscontri problemi o hai bisogno di assistenza dedicata, saremo felici di aiutarti sotto un contratto di supporto. Contatta sales@smartgridone.com per prezzi e disponibilità.
Passo 1
Collega il misuratore al SmartgridOne Controller utilizzando RS485 o Modbus TCP.
- Per Modbus-TCP ethernet: Si prega di seguire le linee guida per il cablaggio ethernet. Per un corretto cablaggio ethernet:
- Per RS485: Si prega di seguire le linee guida per il cablaggio RS485
Controlla anche il manuale del tuo misuratore per i dettagli corretti sul cablaggio e la connessione e verifica se sono necessarie modifiche alle impostazioni per abilitare la comunicazione modbus.
Passo 2
Raccogli le seguenti informazioni dal tuo misuratore di energia:
- Indirizzo Modbus: L'indirizzo del misuratore di energia sul bus RS485.
- Velocità di comunicazione: La velocità di comunicazione del misuratore di energia (es. 9600, 19200, ecc.).
- Parità: L'impostazione di parità del misuratore di energia (es. Nessuna, Pari, Dispari).
- Informazioni sui registri: Per ciascuna misurazione che desideri leggere, avrai bisogno di:
- Indirizzo del registro (in decimale)
- Tipo di dato (es. int16, uint32, float32)
- Ordine delle parole (se applicabile per valori multi-registro)
- Qualsiasi fattore di scala o offset necessario
- Il tipo di misurazione (es. tensione, corrente, potenza)
Passo 3
Apri l'interfaccia web del SmartgridOne Controller e naviga alla sezione di configurazione del misuratore di energia. Quindi, trova il driver "Generic":

Seleziona l'interfaccia che desideri utilizzare (RS485 o Modbus TCP).
Passo 4:
Dovrai fornire una configurazione JSON che definisce quali registri leggere e come interpretarli. La configurazione segue questa struttura:
[
{
"dataType": "float32",
"address": 3000,
"wordOrder": "bigEndian",
"scaleFactor": 1,
"measurement": "actualPowerTot_W"
},
{
"dataType": "uint32",
"address": 3002,
"wordOrder": "bigEndian",
"scaleFactor": 0.1,
"measurement": "importedAbsEnergyTot_Wh"
}
]
Ogni configurazione del registro richiede:
dataType: Il tipo di dato memorizzato nel registro (es. "int16", "uint32", "float32")address: L'indirizzo del registro Modbus in decimalemeasurement: Il nome di misurazione standardizzato (es. "actualPowerTot_W", "importedAbsEnergyTot_Wh")
I campi facoltativi includono:
wordOrder: Come sono ordinati i valori multi-registro ("bigEndian", "littleEndian", "middleEndian", "reverseWord")scaleFactor: Valore da moltiplicare per il valore grezzo del registro (predefinito: 1)offset: Valore da aggiungere dopo la scalatura (predefinito: 0)bytePosition: Posizione all'interno di un array di byte (se applicabile)enumMapping: Per i tipi enum, mappa i valori a stringhelength: Per array o campi byte, numero di elementisigned: Per i tipi numerici, se il valore è firmato
Raccomandiamo vivamente di includere almeno:
- Potenza Totale (
actualPowerTot_W) - Energia Totale Importata (
importedAbsEnergyTot_Wh) - Energia Totale Esportata (
exportedAbsEnergyTot_Wh) se bidirezionale
Inserisci il codice in questo posto:
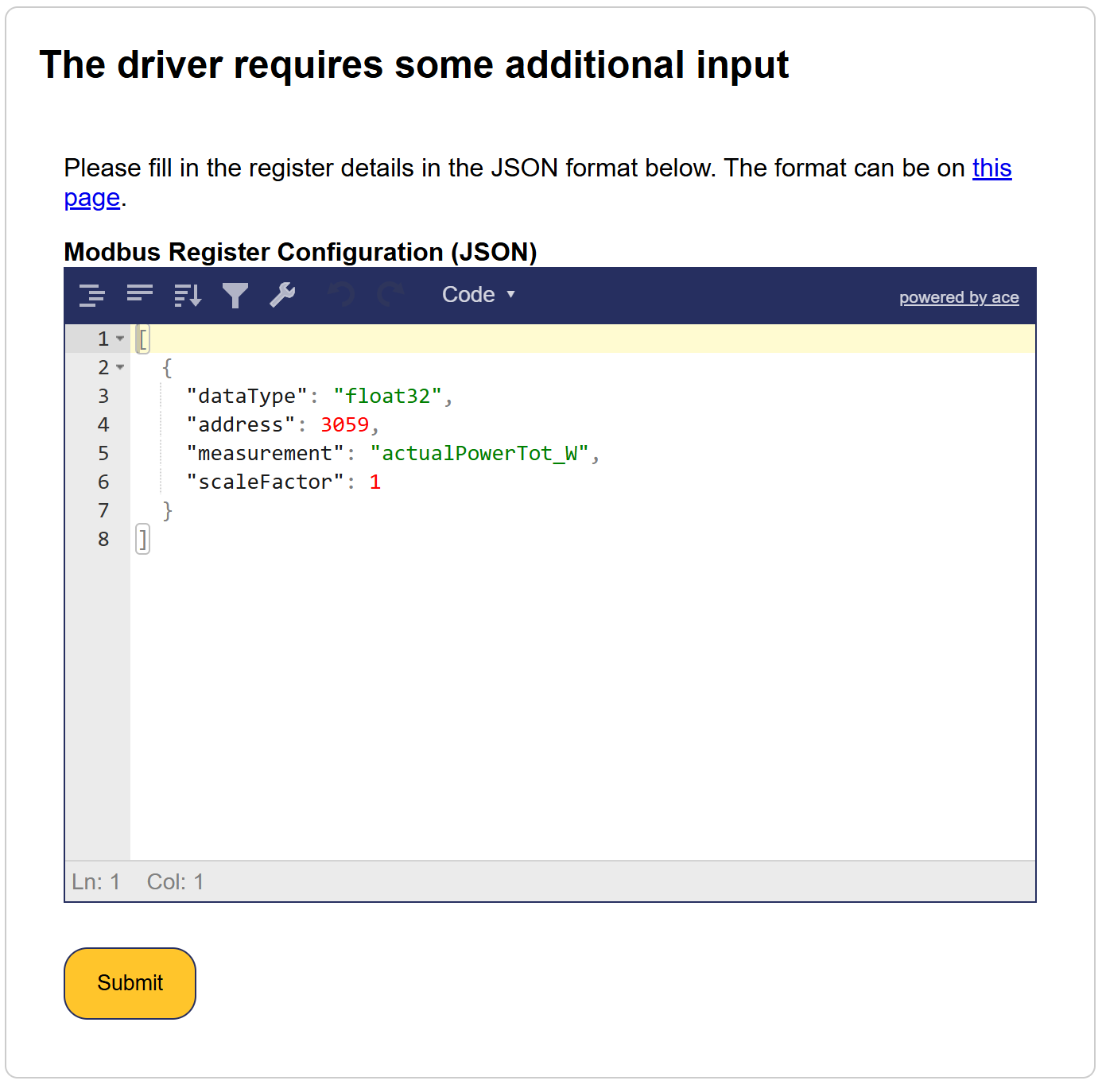
Details
L'input è rigorosamente convalidato e non accetterà errori:
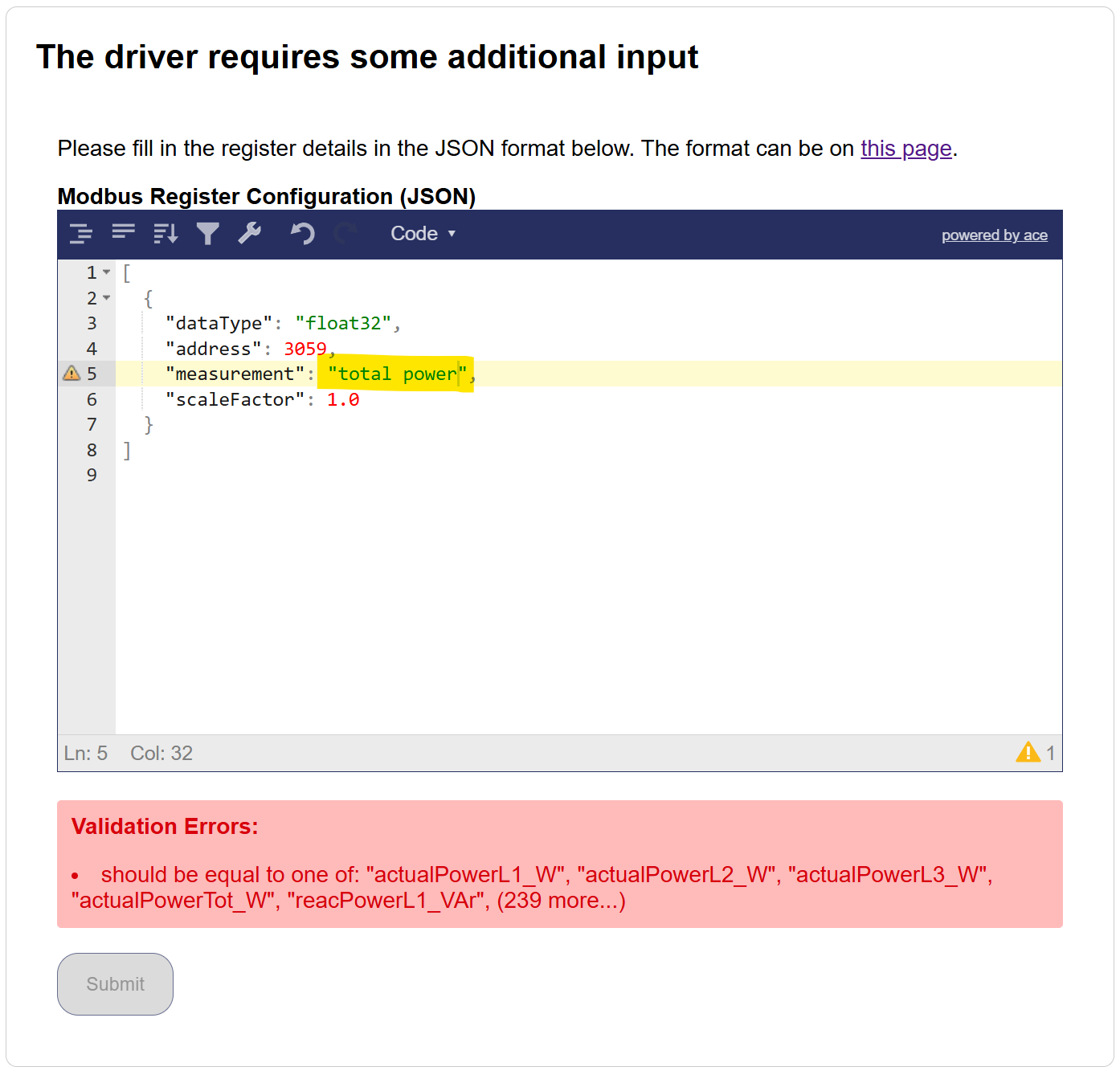
Details
L'esempio sopra non è accettato perché l'utente ha scelto potenza totale invece di actualPowerTot_W.
Le seguenti misurazioni sono accettate:
actualPowerL1_W
actualPowerL2_W
actualPowerL3_W
actualPowerTot_W
reacPowerL1_VAr
reacPowerL2_VAr
reacPowerL3_VAr
reacPowerTot_VAr
importedAbsEnergyL1_Wh
importedAbsEnergyL2_Wh
importedAbsEnergyL3_Wh
importedAbsEnergyTot_Wh
importedEnergyTodayTot_Wh
importedAbsReacEnergyL1_VArh
importedAbsReacEnergyL2_VArh
importedAbsReacEnergyL3_VArh
importedAbsReacEnergyTot_VArh
importedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
grossImportedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
importedReacEnergyDeltaL1_VArh
importedReacEnergyDeltaL2_VArh
importedReacEnergyDeltaL3_VArh
importedReacEnergyDeltaTot_VArh
exportedAbsEnergyL1_Wh
exportedAbsEnergyL2_Wh
exportedAbsEnergyL3_Wh
exportedAbsEnergyTot_Wh
exportedEnergyTodayTot_Wh
exportedAbsReacEnergyL1_VArh
exportedAbsReacEnergyL2_VArh
exportedAbsReacEnergyL3_VArh
exportedAbsReacEnergyTot_VArh
exportedEnergyDeltaL1_Wh
exportedEnergyDeltaL2_Wh
exportedEnergyDeltaL3_Wh
exportedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
grossExportedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
exportedReacEnergyDeltaL1_VArh
exportedReacEnergyDeltaL2_VArh
exportedReacEnergyDeltaL3_VArh
exportedReacEnergyDeltaTot_VArh
producedAbsEnergyL1_Wh
producedAbsEnergyL2_Wh
producedAbsEnergyL3_Wh
producedAbsEnergyTot_Wh
producedAbsReacEnergyTot_VArh
consumedAbsEnergyL1_Wh
consumedAbsEnergyL2_Wh
consumedAbsEnergyL3_Wh
consumedAbsEnergyTot_Wh
consumedEnergyTodayTot_Wh
consumedAbsReacEnergyTot_VArh
producedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
consumedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
producedEnergyTodayTot_Wh
chargedAbsEnergyTot_Wh
chargedEnergyTodayTot_Wh
chargedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
dischargedAbsEnergyTot_Wh
dischargedEnergyTodayTot_Wh
dischargedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenProducedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenConsumedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenLoadsPower_W
childrenLoadsImpEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenLoadsExpEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenOtherPower_W
childrenOtherImpEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenOtherExpEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenUnmeasPower_W
childrenUnmeasImpEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenUnmeasExpEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenProducedPower_W
childrenConsumedPower_W
childrenStoragePower_W
childrenEVPower_W
childrenHVACPower_W
autoconsumedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
producedExpEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenStorageChargedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenStorageDischargedEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenStorageSolarChargeEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenStorageGridChargeEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenStorageSolarDischargeEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenStorageGridDischargeEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenEVChargeEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
childrenHVACEnergyDeltaTot_Wh
currentL1_A
currentL2_A
currentL3_A
currentN_A
currentLAvg_A
voltageL1N_V
voltageL2N_V
voltageL3N_V
voltageLNAvg_V
voltageL1L2_V
voltageL2L3_V
voltageL3L1_V
voltageLLAvg_V
frequency_Hz
powerFactorTot
powerFactorL1
powerFactorL2
powerFactorL3
voltageDCBus_V
voltageInput1_V
currentInput1_A
powerInput1_W
voltageInput2_V
currentInput2_A
powerInput2_W
voltageInput3_V
currentInput3_A
powerInput3_W
voltageInput4_V
currentInput4_A
powerInput4_W
voltageInput5_V
currentInput5_A
powerInput5_W
voltageInput6_V
currentInput6_A
powerInput6_W
voltageInput7_V
currentInput7_A
powerInput7_W
voltageInput8_V
currentInput8_A
powerInput8_W
voltageInput9_V
currentInput9_A
powerInput9_W
voltageInput10_V
currentInput10_A
powerInput10_W
voltageDC_V
currentDC_A
voltageInputA_V
currentInputA_A
powerInputA_W
voltageInputA1_V
currentInputA1_A
powerInputA1_W
voltageInputA2_V
currentInputA2_A
powerInputA2_W
voltageInputA3_V
currentInputA3_A
powerInputA3_W
voltageInputA4_V
currentInputA4_A
powerInputA4_W
voltageInputA5_V
currentInputA5_A
powerInputA5_W
voltageInputA6_V
currentInputA6_A
powerInputA6_W
voltageInputB_V
currentInputB_A
powerInputB_W
voltageInputB1_V
currentInputB1_A
powerInputB1_W
voltageInputB2_V
currentInputB2_A
powerInputB2_W
voltageInputB3_V
currentInputB3_A
powerInputB3_W
voltageInputB4_V
currentInputB4_A
powerInputB4_W
voltageInputB5_V
currentInputB5_A
powerInputB5_W
voltageInputB6_V
currentInputB6_A
powerInputB6_W
currentInputTot_A
voltageInputAvg_V
powerInputTot_W
cabinetTemp_degC
ambientTemp_degC
heatSinkTemp_degC
isolationResistance_kOhm
runTimeTot_s
status
statusMsg
workingMode
operationMode
heatingAbsEnergy_Wh
heatingAbsVolume_m3
flowRate_m3ph
thermalPower_W
departureLineTemp_degC
returnLineTemp_degC
chargedAbsSessionEnergyTot_Wh
sessionDuration_s
chargingSessionId
evNumOfPhases
evUsedPhases
evTargetACChargeCurrent_A
evRequiringCharge
remainingEnergy_Wh
batteryVoltage_V
batteryCurrent_A
batteryPower_W
batteryTemp_degC
batteryOperationMode
PVOperationMode
gridOperationMode
current_A
consumedEnergy_Ah
stateOfCharge_frac
powerSetpoint_W
minStateOfCharge_frac
stateOfHealth_frac
storedEnergy_Wh
absVolume_m3
volumeDelta_m3
flow_m3ps
absPulseCount
pulseCountDelta
pulseRate_ph
flow1_m3ps
flow2_m3ps
flow3_m3ps
flow4_m3ps
flow5_m3ps
flow6_m3ps
flow7_m3ps
flow8_m3ps
flow9_m3ps
flow1_Lps
flow2_Lps
flow3_Lps
flow4_Lps
flow5_Lps
flow6_Lps
flow7_Lps
flow8_Lps
flow9_Lps
Passaggio 5
Dopo aver compilato le informazioni richieste, salva la configurazione.
Il SmartgridOne Controller tenterà ora di comunicare con il contatore d'energia utilizzando le impostazioni fornite.
tip
Per una migliore organizzazione, puoi creare prima la tua configurazione JSON in un editor di testo, quindi incollarla nel campo di configurazione. Questo rende più facile modificare e convalidare la struttura prima di applicarla.